Tl;Dr
- BTCfi is thriving, and it’s largely due to some unique technological innovations over the past few years.
- SegWit increased block space, while Taproot brought smart contract functionality.
- These innovations led to the rise of Ordinals, BRC-20, and Runes.
- Babylon pushed further by igniting the BTC staking revolution to bring yields to holders.
- Layer-2s continue the innovation by bringing scalability and programmability to Bitcoin.
It’s been a wild ride for Bitcoin in 2024. The BTC ecosystem is currently in full-throttle mode as it attracts thousands of builders in the BTCfi space, and this is largely a result of technological innovation in the Bitcoin codebase.
BTCfi stands for BTC DeFi, a new trend of decentralized finance applications built directly on the Bitcoin blockchain.
The year started on an optimistic footing with the SEC approving eleven ETFs, and it continued with the BTC halving and the advancement of the BTCfi world. With all eyes on Bitcoin, let’s take a look at some of the new tech that has led to the emergence of BTCfi.
A Quick Look at the Bitcoin Block Halving Halving
Before we get started on the tech side, let’s take a look at Bitcoin’s monumental fourth halving—after all, the Bitcoin block halving is a technology that is baked into the code and scheduled to occur every four years on average.
The fourth halving occurred in April 2024, reducing the block reward (the subsidy provided to miners that secure the network) to just 3.125 BTC per block. Since the halving, the hash rate has largely remained flat, bouncing between 600 EH/s and 700 EH/s:
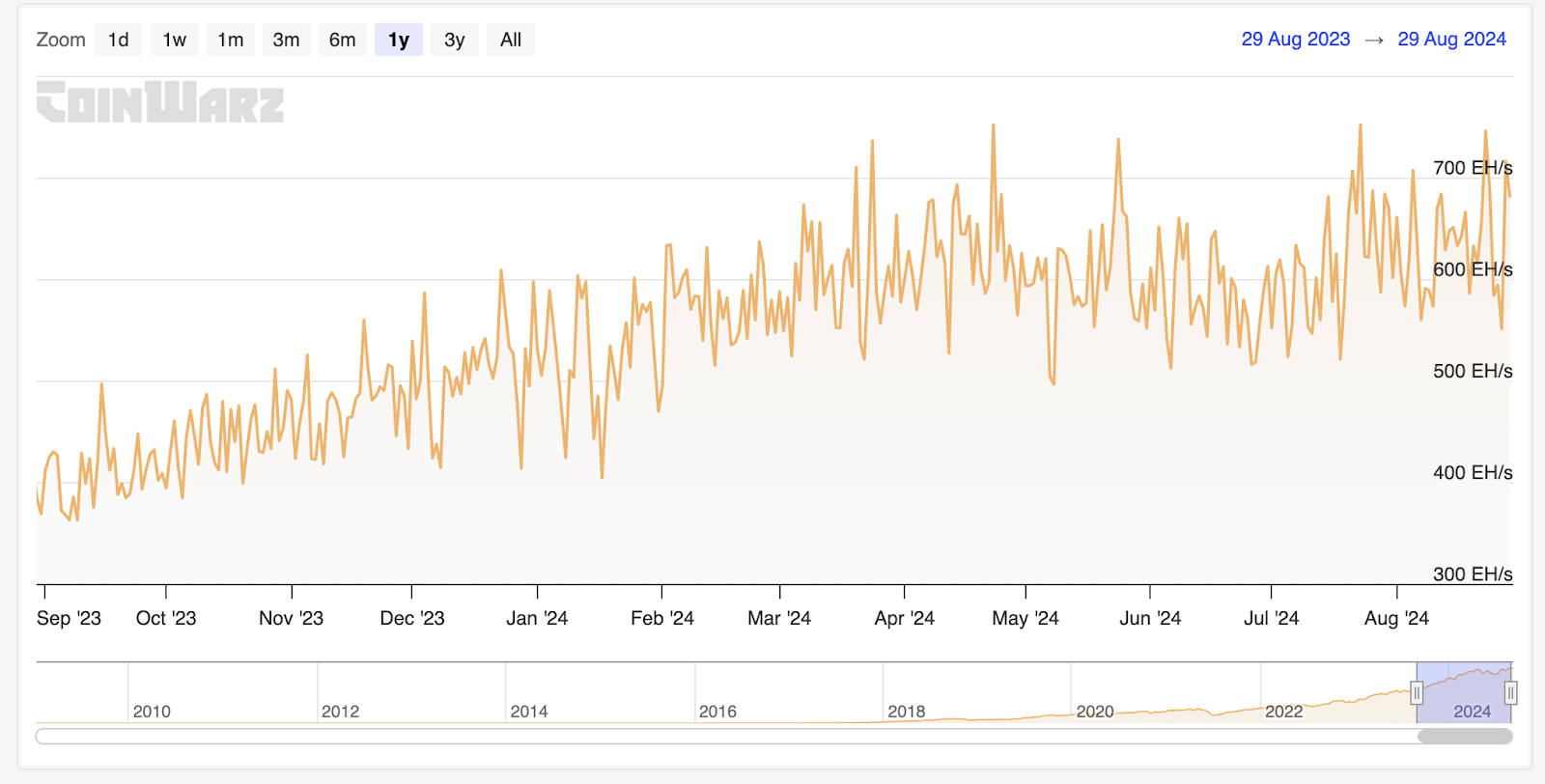
While you might think that mining revenues might have drastically decreased following the fourth block halving, you’d be surprised to learn that they’re actually going up. While BTC rewards fall, the revenue in terms of US dollar value increases.
The following chart shows the growth of Bitcoin mining over time, and it shows that miners are still experiencing surges of revenue growth as a result of the extreme bull and bear markets in BTC:
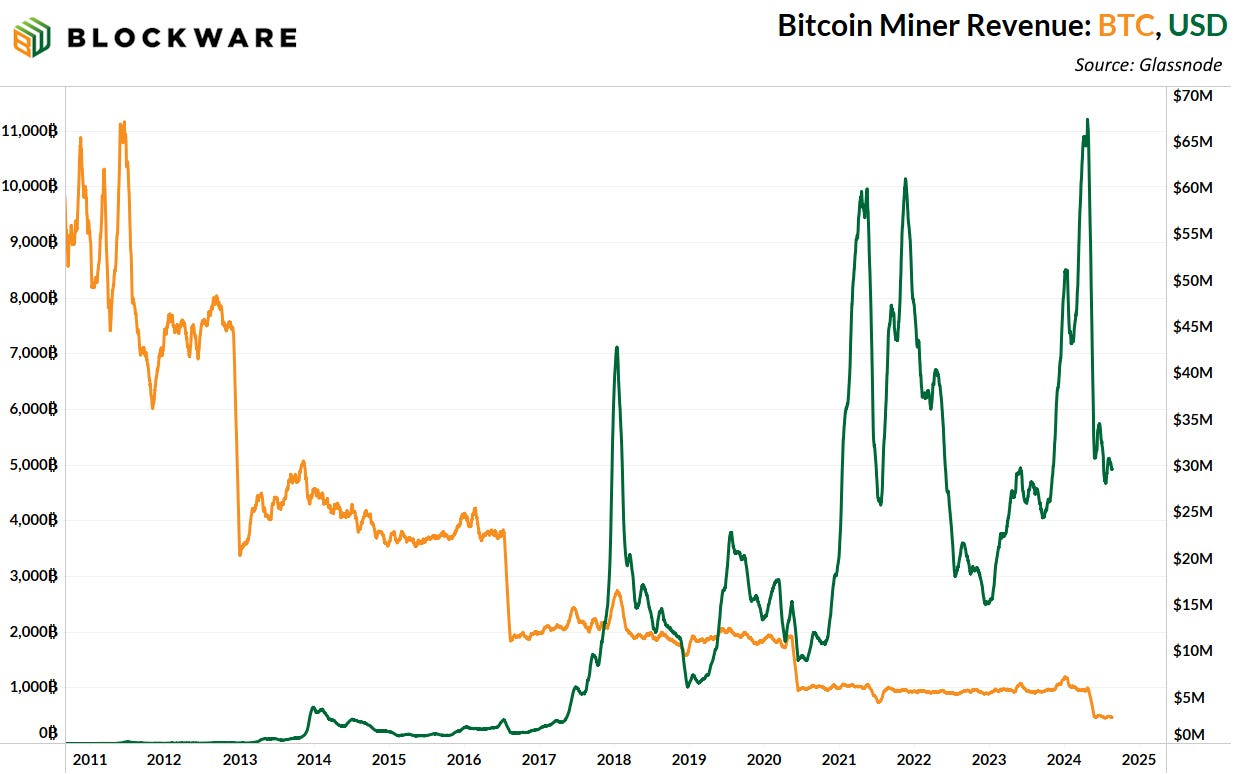
This is good news as it shows that miners are still making substantial revenues, which will be an important incentive to continue securing the chain to allow for the most robust security in BTCfi.
SegWit: Segregating Witness Data and Transaction Data.
The initial genesis point of the BTCfi wave could be pinpointed to the Taproot upgrade in November 2021. However, many experts believe that the SegWit upgrade in October 2017 was actually the first domino to fall, leading to the growth of BTCfi today.
The Bitcoin Core development team introduced the Segregated Witness (SegWit) upgrade in October 2017, allowing the block size for each Bitcoin block to contain 4x more data than previously. The increase to 4MB storage in each block made room to create the building blocks that developers would require in the years to come. It would also help improve transaction speeds and flows by including more transactions in each block.
SegWit altered the way that witness nodes signed transactions. By dividing the transaction into the Witness data and the original structure (sender and receiver data), blocks were segregated by removing the signature outside the transaction data, reducing the size required for transaction storage.
Taproot: Bringing Smart Contract Functionality to Bitcoin
Following SegWit’s success came Taproot, an upgrade that occurred in November 2021. Taproot was a set of protocol improvements that helped to streamline transaction processing, improving efficiency for speed and cost. By batching multiple signatures and transactions together, the Taproot soft-fork upgrade made it easier to verify transactions.
The upgrade was made possible through Schnorr signatures (BIP 340), which allowed a sum of public keys to sign a sum of signatures, allowing Bitcoin transactions to be verified in batches instead of one at a time. It also made Bitcoin digital signatures more secure, efficient, and backward compatible, which is why the upgrade was a soft fork instead of a hard fork.
In addition to the Schnorr signatures, the Taproot upgrade also included BIP 342 – Tapscript. This BIP updated the original scripting language, paving the way for smart contracts to be implemented on the Bitcoin codebase.
Ordinals: Bringing a Wave of NFTs to Bitcoin From Taproot
Bitcoin Ordinals brought programmability to the blockchain by providing new ways of storing text, images, and other data on the Bitcoin network itself. This was largely a result of the SegWit and Taproot upgrades.
Casey Rodarmor founded the technology, which was launched in January 2023. Ordinals are essentially NFTs on the blockchain created through inscriptions onto satoshis (the smallest unit of BTC). The technology is based on Ordinals theory, which states that every Satoshi is allocated a serial number depending on the order in which it was mined. These ordinals give each Satoshi a unique ID, meaning they can easily be tracked on the blockchain.
Users wanting to create NFTs on the Bitcoin blockchain would inscribe their content on top of the satoshis and embed them into Bitcoin blocks. The inscription would utilize the Taproot output, which would be spent to reveal the inscribed content.
Bitcoin Ordinals created a wave of excitement as they are Bitcoin-native NFTs, meaning they sit right on the Bitcoin network itself without requiring a secondary layer. As there was a 4MB limit, text and images were easily inscribed and added to the blockchain. This brought a wave of excitement to the BTCfi world, causing a huge surge in the number of transactions at the time – and things haven’t been quite the same ever since:
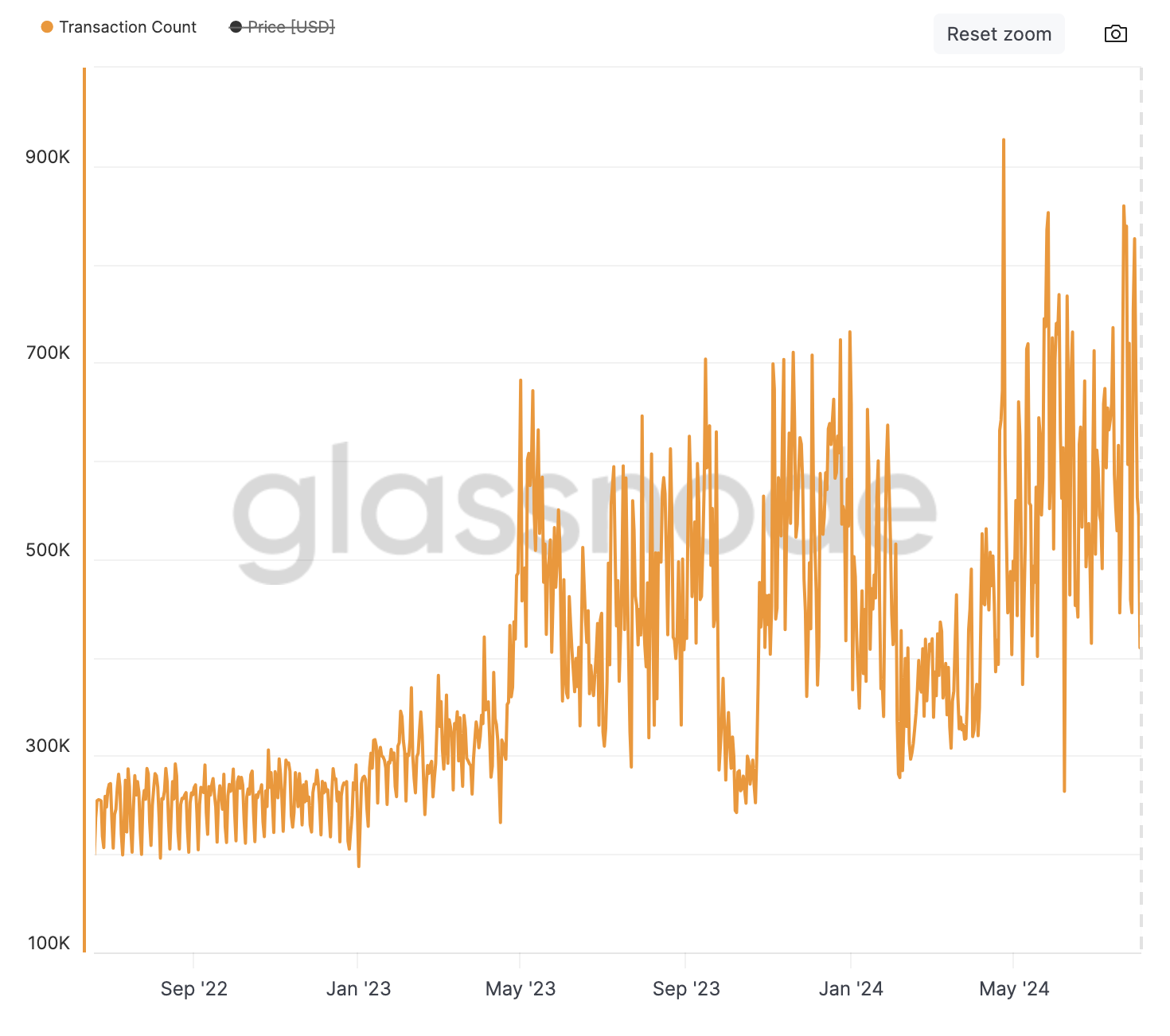
The Ordinal’s discovery evolved into Runes, again founded by Casey Rodarmor (the creator of Ordinals). Launched in April 2024, Runes allowed for the creation of fungible tokens on the Bitcoin blockchain using Bitcoin’s native UTXO model and the OP_RETURN opcode.
UTXOs are Unspent Transaction Outputs representing the quantity of BTC that remains unspent. It’s the wallet owner’s output of a previous transaction until it is used in another transaction. UTXOs are native to the Bitcoin codebase, and Runes are assigned to a UTXO through Runestones, allowing new token creation.
Runes elevated the BTCfi world by solving the problem of “junk” UTXOs and reducing blockchain bloat, making the issuance of assets on the Bitcoin blockchain more streamlined.
Babylon: Bringing Native Staking to BTC
That brings us to today when Babylon Labs turned BTC into an active yield-generating asset through staking. As Bitcoin runs on a proof-of-work (PoW) consensus mechanism, it has no native staking facility. Well, Babylon came up with an innovative solution that utilizes the features of the Bitcoin codebase to turn BTC into a slashable asset.
Babylon figured out a solution that turned BTC into a slashable asset by applying an extractable one-time signature (ETOS). By turning BTC into a slashable asset through Bitcoin UTXO burning, BTC can be utilized to add economic security to proof-of-stake (PoS) chains to receive rewards for security. Babylon also utilizes the built-in time-locking feature on the Bitcoin network, allowing users to lock BTC for a specific period of time and unlock it without relying on a third party.
As a result, Babylon opened the doors to native BTC staking, changing Bitcoin’s value proposition from a store of value to a yield-generating asset—truly bringing BTCfi to life!
New Innovations: Scalability and Programmability
As a result of the innovation on top of the Bitcoin network in the past few years, builders are flocking to Bitcoin in droves as they seek to bring speed and smart contracts to the Bitcoin network through Layer 2s or Sidechains. There are now dozens of these projects in the BTC ecosystem, all bringing their unique features to the BTCfi world that aim to provide Bitcoin with more versatility in the DeFi world.
While dozens of these projects have emerged, here are two of the most notable upgrades that are bringing new technologies to Bitcoin:
Stacks: Nakamoto Upgrade
Stacks is described as the leading layer-2 network for Bitcoin, designed to bring faster transaction speeds, smart contracts, and DeFi applications. Stacks is anchored into Bitcoin and utilizes it as a settlement layer for Stacks.
One notable tech upgrade coming to Stacks is the Nakamoto upgrade. Dubbed the most significant upgrade to Stacks since its launch, Nakamoto is a new consensus system that will introduce faster blocks, enable Perpetual protocols, enhance on-chain payment services, and introduce new DeFi primitives.
For more information, check out this detailed breakdown of the Nakamoto upgrade from Muneeb Ali, Co-Founder of Stacks.
Tap Protocol: First-Ever Bitcoin-Native Smart Contracts
Tap Protocol is another Bitcoin Layer 2 that’s creating waves in the BTCfi space. Tap Protocol is a Bitcoin Ordinals protocol that improves on the BRC-20 standard designed to track and find Oridnals. It also provides a new route to bringing programmability to the Bitcoin world, with 50 projects already directly built on its network,
Tap Protocol is an innovator in the space after executing the first-ever Bitcoin-native smart contracts, swaps, and liquidity pool on the Bitcoin L1 mainnet. This groundbreaking achievement allows DeFi applications to function on Bitcoin’s mainnet without requiring a Layer 2 solution or a sidechain.
Persistence One: Bringing the BTCfi World Together Through Interoperability
As you can see, the innovation and technology in the Bitcoin world never sleeps. However, with the BTCfi world rapidly emerging, the industry is still very fragmented, as many BTC variants and derivatives live on different chains and networks and cannot be easily swapped. Interoperability between the networks will be a huge component of BTCfi’s accelerated growth, much as it was with the emergence of Ethereum DeFi.
Persistence One is working to remedy the effects of fragmentation through an interoperability solution that will make moving BTC (and its variants) around more seamless. We intend to become a major venue for cross-chain BTC swaps through an intent-based solution, which allows users to specify the outcome of their desired swap without having to specify the route.
In turn, Solvers (market makers) can utilize their unified sources of liquidity to fill the trade. As a result, the Persistence One interoperability solution will allow the many emerging BTC tokens on Layer 2s and sidechains to easily be swapped between one another, allowing users in the ecosystem to easily onboard/offboard to different ecosystems in the space.
About Persistence One
Persistence One is building a Bitcoin interoperability solution to enable cross-chain BTC swaps across Bitcoin Layer 2s.
The rapid rollout of Bitcoin L2s and side chains has led to fragmentation, hurting BTCfi scalability. Using the power of intents, Persistence One will enable users to move assets across Bitcoin Layer 2s more efficiently than traditional bridging, offering fast, secure, zero-slippage cross-chain swaps.
Twitter | LinkedIn | Telegram | YouTube | Reddit | [email protected]





